
Developers wanting to develop AI, can use machine learning libraries like Google's TensorFlow or Facebook's PyTorch.
Both libraries can be used for neural networks' machine learning applications, such as computer vision and natural language processing. Both being open-source software, they are like gifts for developers and alike.
And here, China's Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd. is jumping into the bandwagon, by open-sourcing its own AI-based application development called 'MindSpore'. First introduced in August 2019, Huawei wants to make the scalable, cloud-based framework a direct competitor to both TensorFlow and PyTorch.
Quoted in the Huawei's announcement, the company's Chief Scientist Chen Lei said that:
Huawei developed MindSpore with partners, including Imperial College London, Peking University and the University of Edinburgh, as well as a Turkish robotics startup called Milvus.
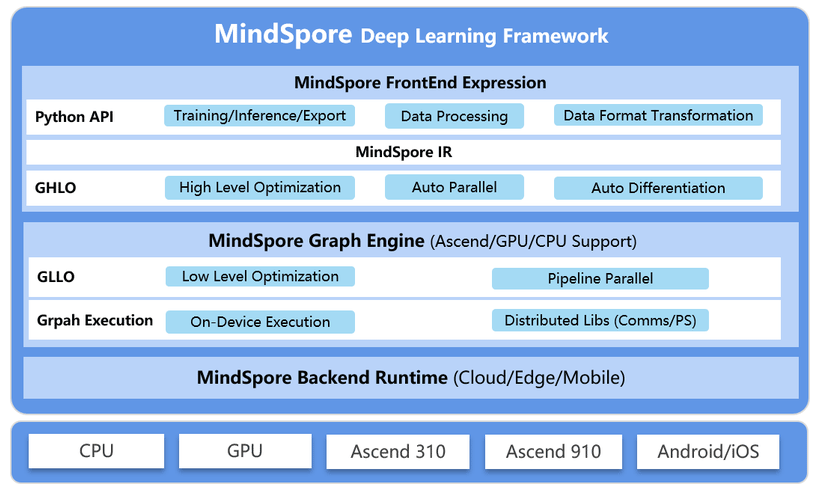
The framework is said to run atop processors, graphics cards and specialized neural processing chips such as Huawei’s own Ascend AI hardware.
Available for download on both GitHub and Gitee, Huawei boasts MindSpore as having several advantages to others that lead the competition.
For example, Huawei said that it's MindSpore uses about 20% fewer lines of code than other competing AI frameworks for tasks such as natural language processing, and the company claims that this can lead to an average efficiency boost of 50%.
In addition, MindSpore is said to support parallel training across hardware to cut down on training times, as well as dynamic debugging, which makes it easier for developers to isolate any bugs in their apps. This again can cut down AI training time.
Another key advantage of MindSpore is that it doesn’t process any data by itself but rather ingests just the gradient and model information that has been processed. This way, it can preserve the integrity of sensitive data in even "cross-scenario" environment, while also ensuring that the models remain robust.
Alongside MindSpore, the company also announced that it’s open-sourcing a module called MindInsight, which provides additional debugging and tuning functionality by creating visualizations of the AI training process.
Those visualizations include model parameter information, like training data and accuracy, as well as training progress metrics and computation graphs, said Huawei. There’s also another module called MindArmour, which helps to enhance model security.
MindSpore initially requires Python 3.7+ programming language to run, with Huawei planning to add support for other languages such as C++, Rust and Julia.
It added that the framework runs most efficiently on Linux platforms such as EulerOS and Ubuntu.
Huawei’s decision to open source its MindSpore is part of the company’s wider strategy to cope with being cut off from the Android ecosystem by the U.S. government, which blacklisted the company over security concerns.
By having the code open-sourced, Huawei is simply doing its service to both the community and to the open source ecosystem in general. Because AI is trending and has become a key capability to have, Huawei's move can disrupt the competition that is mostly occupied by Western-based companies.
Huawei isn’t the only company from China that is taking the AI trend seriously. Chinese search engine giant Baidu, for example, has also offered its own open-source AI framework, called PaddlePaddle, since 2017.