
Both the FBI and NSA deal with information. That means the two agencies may have to dig deep into the web when analyzing something.
The web is not a safe place to be, simply because it's already riddled with malicious activities. From malware-ridden websites, phishing campaigns by hackers, defaced websites, and more.
And here, the two agencies published a joint security alert containing details about a strain of Linux malware that the two said was developed and deployed by Russian hackers.
The two agencies said that Russian-backed hackers named Drovorub, has been using the malware in real-world attacks to plant backdoors inside hacked networks.
Based on evidence the two agencies have collected, FBI and NSA officials claim that authors behind the malware is APT28 (Fancy Bear, Sednit), a codename given to a hacker group operating out of military unity 26165 of the Russian General Staff Main Intelligence Directorate (GRU) 85th Main SpecialService Center (GTsSS).
Through their joint alert, the two agencies hope to raise public awareness in both private and public sectors so IT administrators can quickly deploy detection rules and prevention measures.
On their report, the agencies jointly said:
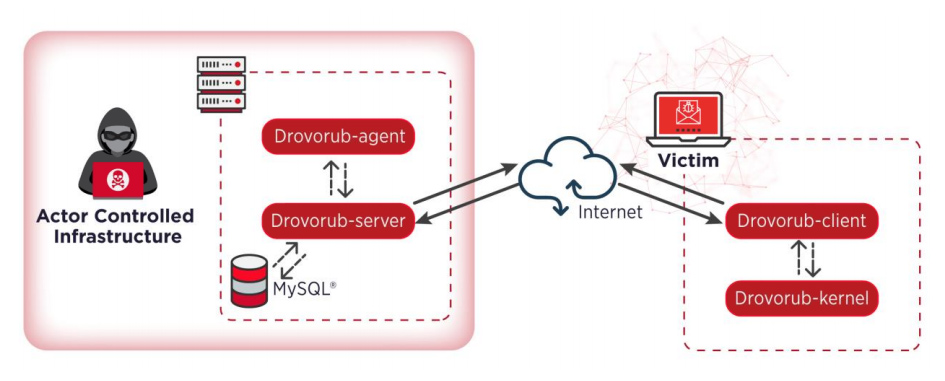
Its suite comprised of following four executables:
- Drovorub-agent.
- Drovorub-client.
- Drovorub-server.
- Drovorub-kernel module.
Drovorub utilizes advanced rootkit technologies, which makes it difficult to detect, as explained by a McAfee executive.
Using its multi-component system, Drovorub is like the swiss-army knife for infecting and stealing.
The agencies added that:
"While packet inspection at network boundaries can be used to detect Drovorub on networks, host-based methods include probing, security products, live response, memory analysis, and media (disk image) analysis."
The name Drovorub comes from a variety of artifacts discovered in Drovorub files and from operations conducted by the GTsSS using this malware; it is the name used by the GTsSS actors themselves. "Drovo" itself translates to “firewood”, or “wood”. "Rub" translates to "to fell”, or “to chop.”
Together, they translate to “woodcutter” or “to split wood."
To prevent Drovorub attacks, the agencies recommend that organizations update any Linux system to a version running kernel version 3.7 or later, "in order to take full advantage of kernel signing enforcement," a security feature that would prevent APT28 hackers from ever installing Drovorub's rootkit.
Additionally, system owners are also advised to configure systems to load only modules with a valid digital signature. This should make it more difficult for hackers to introduce a malicious kernel module into the system.