The internet is a huge place that consists of many networks within networks. With the many people using it, everyone is connected to it - from the good people to the bad, everyone is there.
If you're concerned about internet privacy, there are ways to ensure that outsiders don't gather information about you and your online activity. There are methods which will conceal your identity, making you appear as someone else, or in a different location.
The methods requires something that takes the role of an intermediary - something that is between you and your target. They intercept your data, do what they have to do to anonymize you, before allowing you to retrieve what you asked for.
For you that is not happy with the nature of the web where IP addresses are exposed and identity able to be tracked, the question is: "what should I use?" Or "what is the best that suits my needs?"
There are three popular means to conceal your real identity. Although they perform similar function, the actual process involved a very different method. Each have their own advantages and disadvantages. With the right strategy and combo, you can be sure that you are anonymous wherever you are on the web.
Proxy Servers
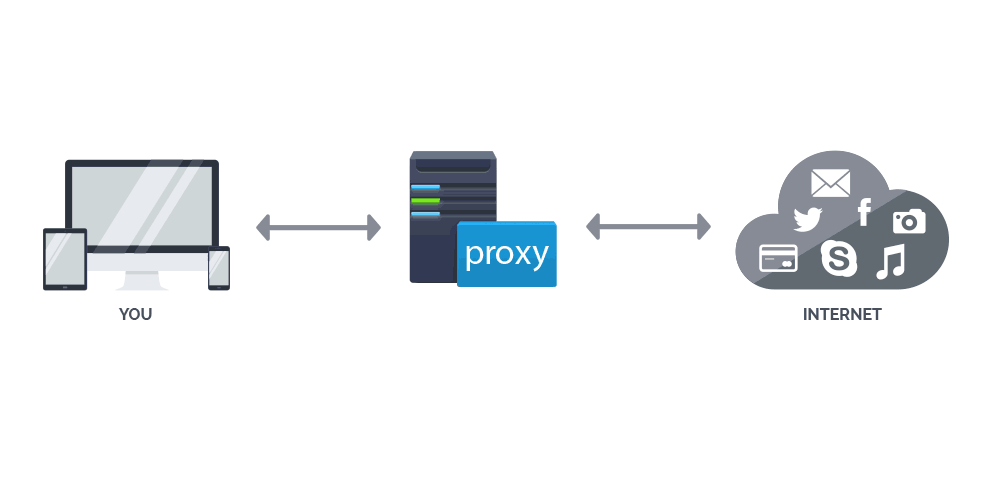
A proxy is a server (a computer system or an application) that acts as an intermediary for your requests by seeking resources from other servers. When you're connected to a proxy server and requesting something on the web such as opening a web page or downloading a file, the proxy server will evaluate your request as a way to simplify and control its complexity.
Proxies add structure and encapsulation to distributed systems, and as most modern proxies are web proxies, they can facilitate access to the World Wide Web and providing anonymity at the same time. When connected to a proxy, your traffic and online activity will be routed to a proxy server, and will appear to come from its IP address, not your computer's.
Proxies are usually cheap and many are offered for free. And because each proxy typically can handle tens of thousands connection, the simultaneous connection is easily available for use. But not every connection can pass through proxies and they can't encrypt all traffic that passes through them.
Proxy servers usually communicate with the internet using one of the two protocols: HTTP or SOCKS.
HTTP proxy servers are designed to handle HTTP protocol which interpret traffic at the HTTP level. What this means is that, all traffic that starts with http:// or https:// (web pages), can use the proxy. This type of proxy is only good for web browsing because all it does, is handling HTTP requests. This method is usually faster than any other types of anonymity connections available for you to use. While this proxy is good to preserve your anonymity, Flash or JavaScript that is shown on many websites, can be made to detect your true IP. Furthermore, HTTP traffic is not encrypted. This means government surveillance systems as well as your ISP can see you. But if you're connected through HTTPS or SSL, then your traffic can't be monitored (IP of the HTTPS can be logged). SSL encryption uses 128-bit key length or equivalent.
The next is SOCKS. These servers don't interpret network traffic at all, which makes them much more flexible. But because they handle more traffic, they tend to be slower. One big advantage of the SOCKS protocol is that it supports any kind of traffic. From HTTP and HTTPS, to POP3 and SMTP for emails, IRC chats, FTP to upload files to web server, and even torrent files.
Public Proxy Servers
Proxy servers can accept so many connections, and this makes many public servers to give their services allowing anyone to use them. Both HTTP and SOCKS servers are available.
The advantage of proxies also provide its own disadvantages. Public proxy servers tend to be highly unstable and can go offline at anytime without notice. They also vary in the speed they offer. Furthermore, you have to trust the owners of the proxy servers because they are the ones that will handle your traffic. Public proxy servers usually come with no support available.
Private Proxy Servers
These proxy servers are not open to the public, and are usually available for a fee. And because you have to pay to use them, they tend to be more reliable because they're run by companies that dedicate themselves for it. Private proxy server also provides comprehensive support for its users.
Web Proxies
Web proxy services connect to public HTTP servers and will allow you to browse the web anonymously within your machine without the needs to download any requirement software or doing any configuration. While they're free, they tend to expose you to a stream of advertising. Web proxies can be reliable and indeed practical, but many people are blocking many well-known web proxies IP addresses from accessing their websites.
VPN
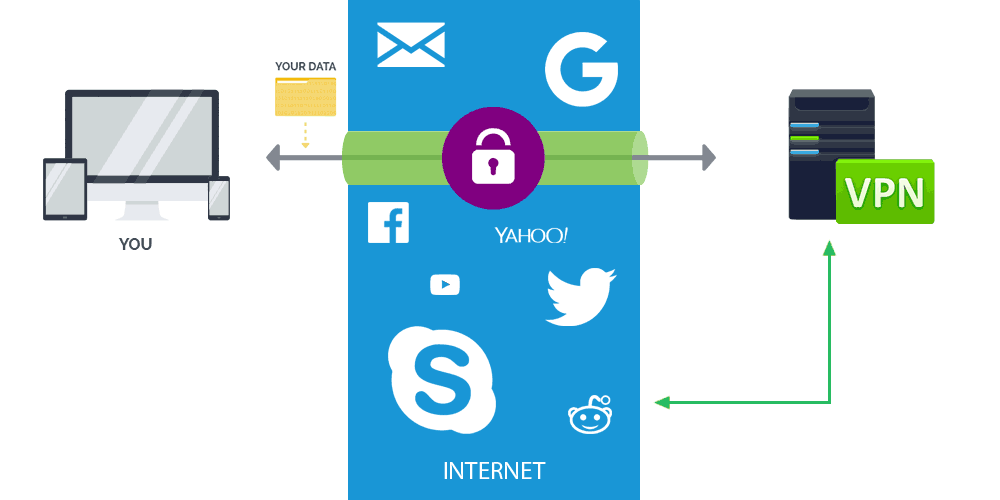
VPN stands for Virtual Private Networks. What it does, is creating a virtual point-to-point connection through the use of dedicated connections, virtual tunneling protocols, or traffic encryption between your machine and the host server. All of your traffic pass through the VPN, enabling you to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network.
By using a VPN, Your ISP or government can only see that you have connected to the VPN server and nothing else. So your activities, IP addresses you have visited and everything else, are completely hidden behind a minimum encryption of 128-bit key length.
A VPN available from the public internet can provide some of the benefits of a wide area network (WAN) so resources available within the private network can be accessed remotely. So beside providing functionality, VPNs also have the security and/or network management benefits.
The advantage of VPNs come with some issues. Some VPN services, especially free ones, can violate your privacy by logging your online activity and usage and making them available for others without your consent. They can also sell your bandwidth to other users. And because VPNs can mask your real IP address and geo-location, many web services are known to block user when they use known VPNs to prevent circumvention. What's more, traditional VPNs are known for their point-to-point topology that don't extend their support or connect to broadcast domains. Services such as Microsoft Windows NetBIOS may not be fully supported or work as they would on local area network (LAN). To overcome this limitation, there are other VPN variants such as Virtual Private LAN service (VPLS) and the layer-2 tunneling protocols.
Before choosing a VPN, it is wise for you to first know who is providing it. The best VPNs are those that are both reliable and don't keep any of your logs.
Both traditional VPNs and VPN services are there to protect you against external visibility into the network. But neither of them will protect you from authorized administrators for the network you're on. VPNs are all about protecting your data from unauthorized eyes. So those that have the authorized privilege, such as the VPNs themselves and the target website, can see the request and log them. So VPN doesn't go well with anonymity, but security is where it's good at.
Using VPN involves setting up a VPN client, or configuring your computer/mobile device. After it is set up, all of you internet traffic, no matter what program you use, will be then routed through the VPN of your choice.
The only notable negatives to VPN are that it is relatively more expensive that proxy servers. And because traffic are encrypted, the process put loads on the servers, slowing down your internet speed.
Tor
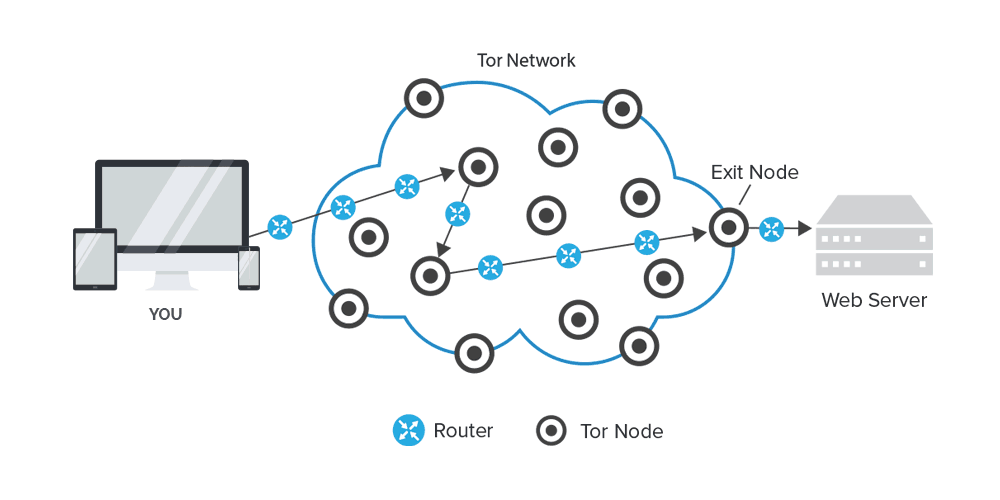
Tor is "The Onion Router". It's a service that allows you to be anonymous when connected to the internet. Unlike proxy servers and VPNs, Tor is a decentralized system that allows you to connect through a network of relays (run by volunteers that are scattered all over the world) rather than making a direct connection.
The benefit of Tor is that your IP address is hidden from practically anything because the method bounces you from one node to another, from server to server at random. On its way, you data is encrypted and decrypted many times before reaching the desired destination and before reaching back to you.
According to the Tor website:
There are disadvantages when using Tor. The first one is speed. Because your data needs to hop numerous times and needs to be encrypted and decrypted just as often, this makes Tor a lot slower than proxies and VPNs. While your data is indeed encrypted and almost impossible to track, the final connection point at the last relay node (the last computer in the Tor network) can be compromised if the requested website does not use SSL (data is in "plaintext").
Furthermore, anyone can setup a Tor exit node and there's nothing to prevent that person from spying on the users.
However, complete anonymity is still accomplished, and this is where Tor excels. With at least 3 nodes to communicate, none of the nodes know the source and destination. Tor does not promise secure communications. Its encryption is only used to provide anonymity between nodes, your data is not encrypted otherwise.
For you that concerns the prying eyes of the government, Tor was created in conjunction with the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory and supported by DARPA, and it is still used by many government agencies. Tor is popular, and is widely used by political dissidents, journalists, and even criminals. For this reason, many governments are careful when they see Tor users, and this could potentially lead you to their attention. Some ISPs in several countries are also active in seeking and blocking Tor relays, making difficult for you to connect.
Tor is an anonymization service that makes it difficult for anyone to trace your internet activity back to you. It's designed with anonymity in mind, and it's free to install and use.
Conclusion
"So which is best?" The answer depends on what you're going to do.
For example, if you just want to bypass a firewall or browse a blocked website in your region, using proxies can be your best way out. It encrypts your data, and puts you on another IP. It doesn't need much configuration and knowledge to set up.
Tor is a good choice if you want to wander the web aimlessly. Together with the Tor browser, for example, you can browse without having any website scripts running (Flash and JavaScript disabled) that can potentially trace you back. You can cross the borders of the web by venturing down the deep web. But the connection using Tor is slower, and by having all your data passing through Tor, you should expect a massive speed decrease. Either proxy or Tor may be sufficient if you just want to surf anonymously.
But if you prefer to have better privacy protection, enhanced security from hackers, identity thieves and malware, and of course better speed, a VPN is likely a better option. But first, you need to make sure that your VPN of choice do keep your data safe or not storing any logs about your activity.
And if you want to feel safer and anonymous, using a combo of two methods like using VPN alongside Tor can be a good choice. The two can benefit one another by adding an extra layer of protection. Here is where Tor is for anonymity and VPN is for security.
However, this will further decrease your speed. VPN is slower than ordinary connection because it encrypts your data, and putting it with Tor with hops your data randomly along relays, will make your speed even slower by margins.
So when again comes the question "which is the best?" The decision is yours.