Google Search is the most popular internet search engine in the world for many reasons.
From its age, founded in 1998, which has certainly given it a head start, to the way it uses complex algorithms, and its extensive use of powerful hardware and carefully placed servers, as well as its undersea projects, Google is pretty much a tech company that nothing can compete with heads on.
But in terms of quality, it somehow degraded.
Google Search has lots of criteria that influences its results. The SEO industry has long been adhering to its rules, in order to make websites rank high, sparking a competition, and also a lucrative business.
However, following the rise of AI, the internet is seeing a massive tidal wave of generative AI content that literally litters the web.
As a result, the heap of spam is 'confusing' Google's algorithms that results become worse.
Instead of filtering out scams, Google is seemingly bowing to the pressure, and is instead promoting these dubious sources.
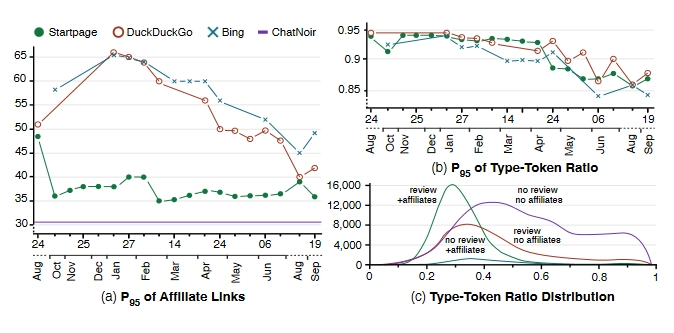
Researchers from Leipzig University, Bauhaus-University Weimar, and the Center for Scalable Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence, have found that Google Search is starting to consistently rank ad-filled spam web pages.
In a year-long study, first reported on by
And here, they found an "inverse relationship between affiliate marketing use and content complexity, and that all search engines fall victim to large-scale affiliate link spam campaigns."
In other words, the "search engines seem to lose the cat-and-mouse game that is SEO spam," the team concluded in their paper (PDF).
Generative AI is said to be playing a central role in the dissemination of this low-quality content, because the technology is making it extremely easy for anyone to create compelling content.
But what's "compelling" doesn't mean "legitimate" or can be "trusted."
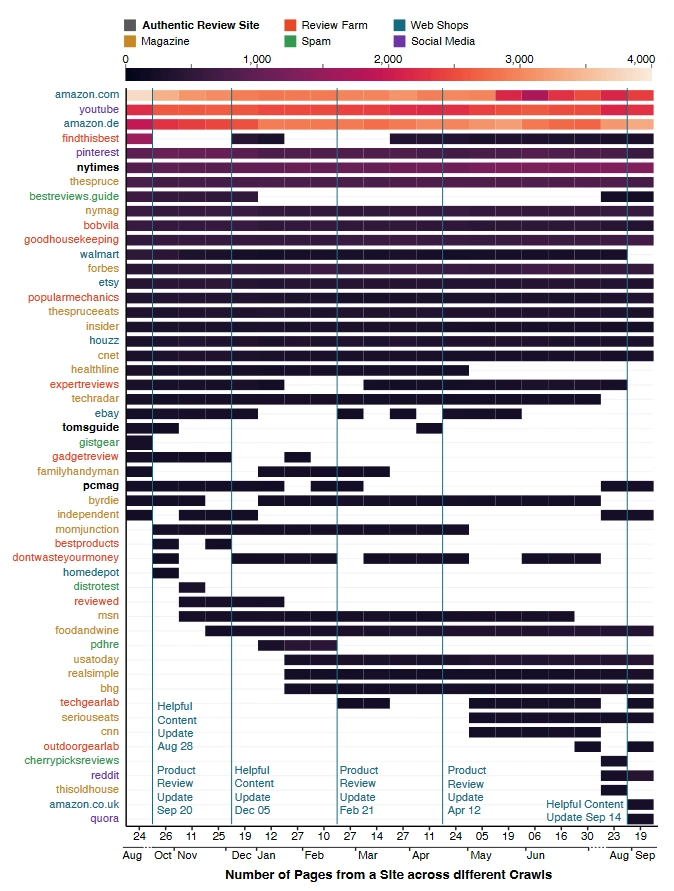
The democratization of AI-powered tools like ChatGPT, a lot of content farms are able to completely automate the processes of SEO spam. Some AI content farms can scan a human-written site, use it for "training data," rewrite it slightly, and then stave off the actual humans with more aggressive SEO tactics.
Doing this, they are able to pump out vast amounts of badly researched and often entirely unedited content, in a short amount of time.
"The line between benign content and spam in the form of content and link farms becomes increasingly blurry — a situation that will surely worsen in the wake of generative AI," the researchers write.
Despite seeing some improvement in results since the start of their experiment in terms of affiliate spam, the team is still seeing a "downwards trend in text quality," which in all leave "quite a lot of room for improvement."
While AI does help people create content, and that it is also mutually beneficial relationship with SEO, the practice of tweaking content to increase its discoverability and have it rank higher on search results, is seemingly confusing Google's algorithms.
Generative AIs are known for their disconnected understanding of the real world, and that they cannot really tell the truth.
But due to how well generative AIs can create text and website posts, Google's algorithms simply promotes those content, because the authors are doing a really good job in SEO.
In the end, Google's own forays into AI-powered search with Search Generative Experience (SGE) is making internet searches a lot more intuitive, the attempt also leaves much to be desired, with the ability to even kill its core product.
The "enshittification" and "junkification" of the internet is real, and generative AI is in big part to blame, the researchers concluded, and the bad news is that it doesn't seem like this will get better any time soon..
In response to the researches, a Google spokesperson pointed out that Google Search is still doing better than its competition.
"This particular study looked narrowly at product review content, and it doesn’t reflect the overall quality and helpfulness of Search for the billions of queries we see every day. We’ve launched specific improvements to address these issues – and the study itself points out that Google has improved over the past year and is performing better than other search engines. More broadly, numerous third parties have measured search engine results for other types of queries and found Google to be of significantly higher quality than the rest."