As long as there are search engines around, SEO will always thrive.
Generally, there are two types of SEO: on-page SEO which deals with contents and page optimizations, and there is off-page SEO which establishes relations with other websites. However, there is a fact that no website can stand without a strong backbone, and apparently, that backbone is technical SEO.
Technical SEO is the structure of your website. It's the thing that's keeping your website together, so you can do on-page and off-page SEO on it.
Without technical SEO, your site should fall apart.
It's one part that should always be present when you audit your site's SEO.
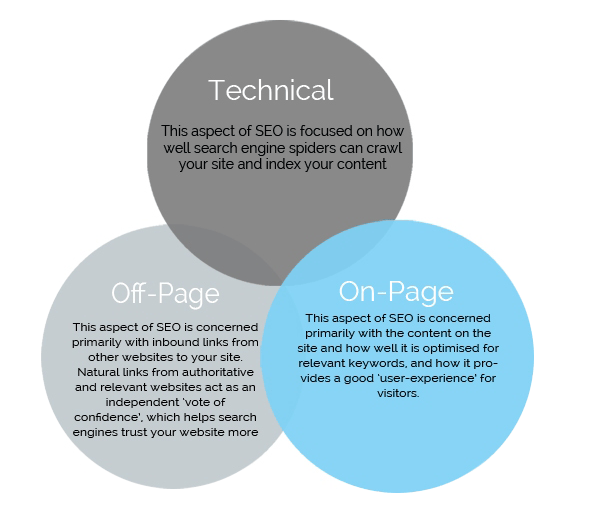
So what is really "technical SEO"?
In short, it is an SEO which provides constant refinements. We know that search engines' requirements change in order to improve. These requirements are challenging and somehow complex. Here, technical SEO is a method to keep up with the search engines, which are getting more sophisticated each day.
For this reason, technical SEO should be optimized to make the necessary foundation that provides your content and links with the best possible marketing environment.
With this, your on-page and off-page SEO can shine in search engines without much of a problem.
Breaking it down to the details:
1. Website Speed

You need to keep your website's templates simple. To do this, limit the components of your website and make the elements minimalists.
Remember that "less is more." Here you need to understand that the more elements your website's page has - from plugins, widgets or tracking codes - the more time it needs to load. If your website fails to load within three seconds, most people will just "bounce" off your website, probably to never return.
Since every website is unique, you need to achieve a healthy balance between the minimum amount of necessary elements, and a complete web design.
Other ways you can optimize you website's speed, is to use CDN, caching solutions, asynchronous loading, Google's AMP and many more.
To start, you may want to understand your website's waterfall diagram first.
Further reading: The Common Practices Of Web Design With Speed In Mind
Visual Optimizations
Images speak a thousand words. Whenever you can, put some images in between your text contents to make things more fun to read and digest. Images attract the eyes better than text, and it also makes viewing a lot pleasant.
In terms of technical SEO, you need to make those images sharp by adjusting the sizes correctly. There should be a balance between a sharp and crisp picture, and a large size heavy to load one.
You should also pick the best format for the need. For example, JPG file format is best for photos, while PNG files are better for graphics, like logos or website design elements.
You may also consider lazy-loading some heavy images to improve your site's performance.
Limiting Redirects
Redirection is to ensure users are seeing the most appropriate content for them, which could be contextualized for their location, language or device.
However, people don't want to jump from one URL to another, and another. This shows inconsistency, incompetence and lack of professionalism. What's more, redirects can badly affect your website's loading speed.
The more redirects installed on one page, the longer a user must wait. This is why you should always reduce the number of redirects to a very minimum, and make sure that you only have a single redirect on a page.
In the case of 404 error pages, when there is a “page not found”, make sure that you have a custom designed page which is user-friendly. Give at least a reason why your user is seeing that page, and guide them back to your home page, or to a popular part of your website.
Browser Caching
When visitors visit your website for the first time, their web browsers start to locally store your website's resources automatically (your logo, CSS files and some others). The reason for this is because the browser wants to speed loading times when the users re-visit your website.
This is why the first view of a page takes longer than repeat visits.
For technical SEO, you need to leverage browser caching, and set it according to your needs.
2. Mobile Friendliness
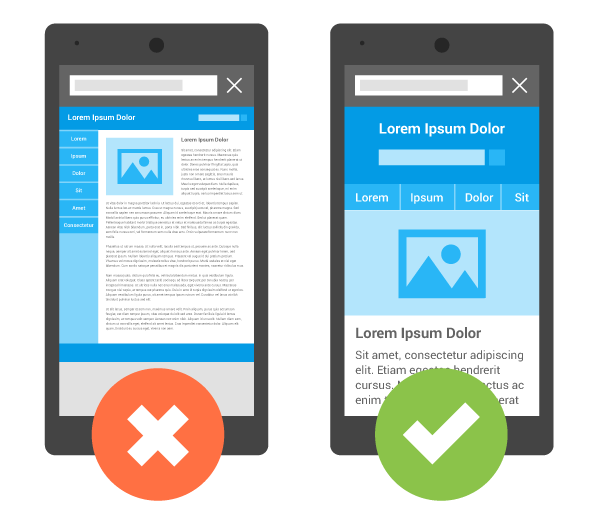
Almost equally as important as website speed, is mobile friendliness.
Since more users are using their smartphones to browse the web, you need to make sure that you can cope with those increasing demands. Google has been putting a lot of attention to mobile friendliness, and since then, mobile-friendly has played an important role on a website's visibility in mobile search, especially for local results.
In order to make your website mobile-ready, you can use responsive web design (RWD) that is tailored to your audience's needs. This design strategy blends to the different width of users' screen, as it adapts its interface to suit whatever device it is viewed on. Or, you can opt for a mobile website which usually resides on a subdomain of your main domain name.
3. Website Architecture
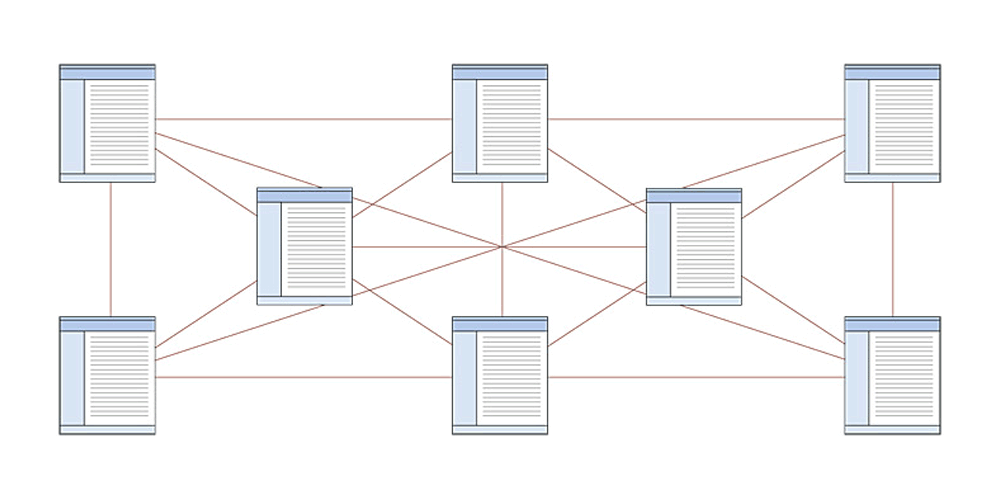
An SEO-friendly website should have a constant website architecture which ensures that you can meet your business goals while delivering a great experience for users. Where information architecture (IA) is a broad field that refers to the structure of any shared system of information, online or otherwise, website architecture relates specifically to websites.
All website’s architecture includes:
- Usability.
- Interaction design.
- User-interface design.
- Information design.
- Web design.
- Graphic design.
- Content strategy.
And in terms of technical SEO, they should all help with SEO friendliness. They include:
Using HTTPS
The right site architecture starts with choosing the appropriate hypertext transfer protocol. In this case, there is only one SEO friendly choice, and that is HTTPS.
Google and other search engines have included HTTPS on their ranking factor lists. The reason for this is because HTTPS ensures all communication that goes out of your website, to be encrypted from anyone. HTTPS communication protocol is encrypted by Transport Layer Security (TLS), or formerly, its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
The protocol is often referred to as HTTP over TLS, or HTTP over SSL.
Read: A Guide To Securing Your Website Using SSL Certificates
Breadcrumbs
A website's breadcrumb or "breadcrumb trail," is a type of navigation that reveals the location of a user. The name itself comes from the Hansel and Gretel fairy tale in which the two siblings left breadcrumbs on their way to the woods in order to be able to find their way back.
This is a type of website navigation strongly enhances the orientational awareness of visitors because it transparently presents the website hierarchy, and indicates where they currently are. What's more, breadcrumbs also reduces the number of actions users have to take to go back to the homepage or a higher level page.
Breadcrumbs are usually present on large websites with complex hierarchy, or websites with many different sections that demand a clear structure.
URL Structure
This introduces a user-friendly, clear and consistent URL structure.
Your website's URL is a readable text that replaces IPs. Here, it describes your page for both users and search engines.
Optimizing your URL structure should act as a ranking factor. For example, if you can make your URL as descriptive and as brief as possible, users should understand what is included on a particular link, before even visiting it. They can know what your page should be about, by just checking on the URL.
Here you can add targeted keyword on that given page to strengthen the relevancy of the whole page and help search engines classify it in the search ranking for that particular keyword.
Proper optimization or your site's URL structure should also help you in creating a proper pagination for your site, a robots.txt file and sitemap(s).
Internal Links
Also called "silo contents", they are all about defining your hierarchy.
They are important to improve visibility of your older pages which may have been buried deep in time. Internal links can also make a page more interesting as it can relate to other pages which are topically related.
You should categorize the website content and always link to the pages within one category. This should ensure that users can scout your website and get the information they need on different pages. This should also lower your site's bounce rate while at the same time, increases your authority on the topic.
4. HTML Markup
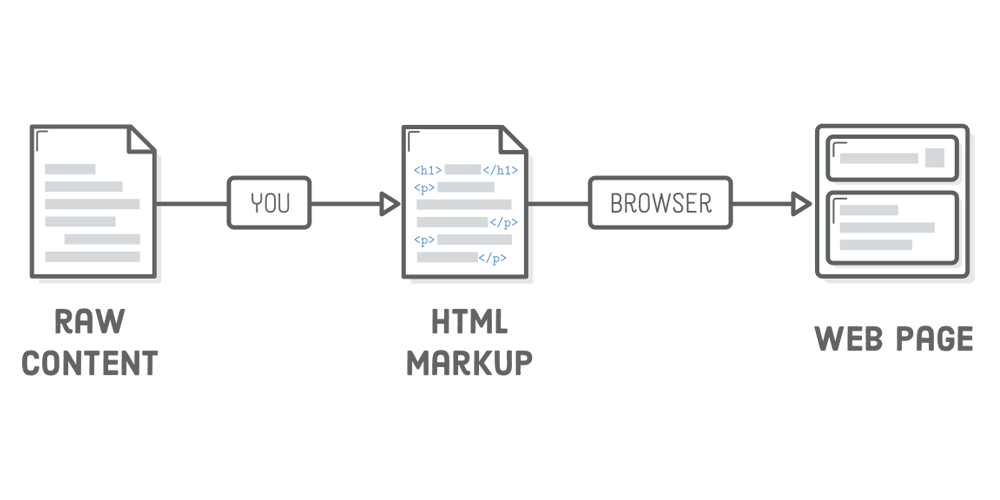
Examples include:
- Open Graph - telling Facebook how your content should appear.
- Twitter Cards.
- Language tags.
- Title, description and header tags.
It also includes structured data markup to show rich snippets in search. Google can identify the intentions of your page by scanning its contents and its on-page optimization resources. However, with the correct structured data markup, Google can being all the information it needs to the next level.
Rich snippets appear in the search results when you type in a specific query.
5. Duplicate Contents
After covering 404 error pages, technical SEO also refers to duplicate contents which are considered a serious issue for search engines.
You can check your website to know whether you have duplicate contents posted. The easiest way is probably by using Google Search Console. And if you see any duplicate contents, you should solve this quickly by either removing the duplicate content entirely, or just rephrase it.
Another strategy is to add canonical URL to those pages with duplicate contents. Canonicalization is the process of choosing a preferred URL when there are several choices for an individual page. This will tell search engines what the source of the published content is and completely resolves the problem.