With the internet in more places and smartphones becoming more capable, many people still use SMS to send messages.
As a matter of fact, billions of people still use the short-messaging service to communicate with their loved ones and colleagues. On the surface, the ubiquitous method has nothing wrong. But when seeing through security perspective, that's a different story
The truth behind SMS is that, the service isn't at all secured.
What this means, not only that the sender and the recipient can read the messages, as third-parties, including the cellular provider can read them plain and clear.
This is why people shouldn't rely on SMS for sending sensitive information or for business confidential.
The first reason is because the underlying technology that powers SMS is old and vulnerable. In the modern days of technology, SMS should be considered an antique method of communication.
But before understanding why you should practice safe texting, you should first understand what is SMS and how the system works in the first place.
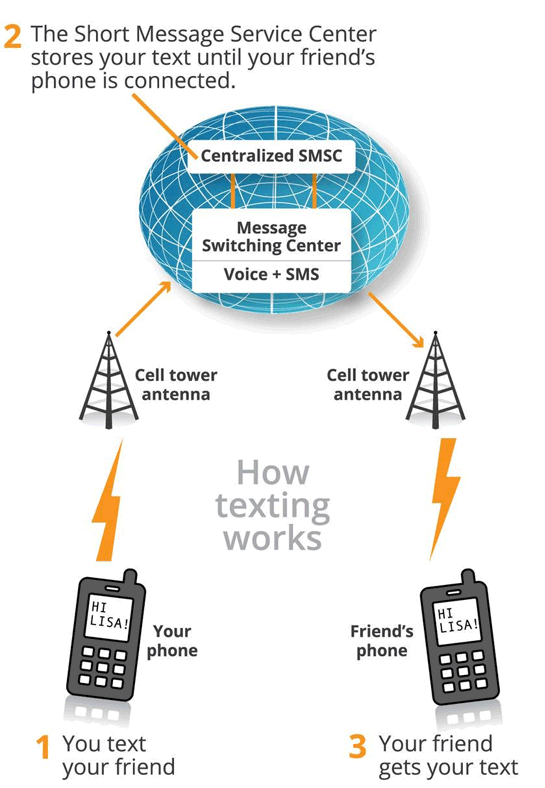
SMS, The Technology Of The 1990s
SMS stands for 'Short Message Service'. As used on modern devices, the underlying technology originated from radio telegraphy in radio memo pagers that used standardized phone protocols. These were defined in 1985 as part of the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) series of standards.
The first SMS message was sent over the Vodafone GSM network in the United Kingdom on 3 December 1992. The text of the message was "Merry Christmas".
The service works like this:
When users send a text message using the SMS feature, the message goes to a nearby cellular tower over a pathway called the control channel, and then into an SMS center (SMSC). The SMSC then resends that message to the cellular tower closest to the recipient, before the tower sends the message to the recipient's phone.
SMS also sends data associated with the message, including the length of the message, format, time stamp, and destination.
Evolving SMS With OTT Apps
With smartphones and internet coverage, people have increased their needs for communication.
And OTT apps are the solutions.
These are simply messaging apps on smartphones, like WhatsApp, iMessage, Facebook Messenger and others. Grouped together, they are called OTT apps, and are also considered texting services.
OTT stands for 'Over the Top'. They are significantly different than SMS because they use internet protocols (IP) rather than cellular networks to transmit messages. What this means, messages sent through these apps are delivered through an internet connection (Wi-Fi or mobile internet connection).
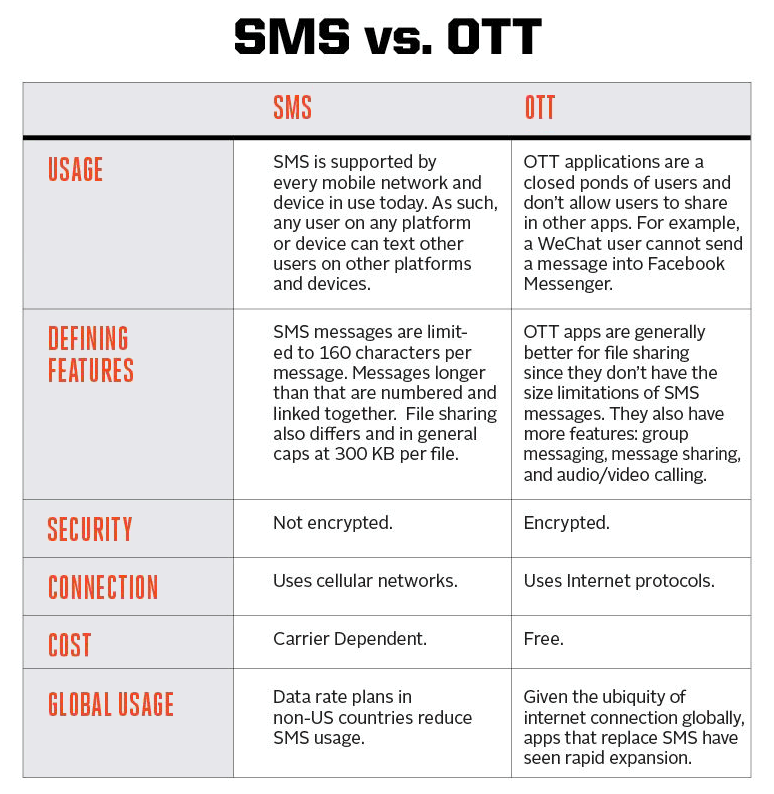
SMS Vs. OTT
With the two having different technologies that revolve in a totally different era, the two certainly have their own advantages and disadvantages.
First of all, SMS is the most ubiquitous. All phones should be able to send messages, as long as the user is within the cellular provider's coverage. Another way of saying it, anyone with a phone can transmit a message to others with a phone.
Even computer servers can be set up to send SMS. This makes the communication method a popular one, and remains as the choice for many.
However, when considering security, SMS is the least secured messaging medium.
Second, OTT apps use the internet rather than cellular coverage, meaning that messages can be encrypted. This way, only the sender and the recipient can read the messages. Others that include the cellular provider can not read them. Adding end-to-end encryption provides stronger security that even the developers of the apps can't read the messages.
In other words, no one should be able to read the messages, even when the web traffic is intercepted. In a security standpoint, this is certainly a huge benefit from SMS.
On the downside, OTT apps require both the sender and the recipient to be using the same platform. For example, someone who uses WhatsApp can only send messages to others that also use WhatsApp. If the recipient doesn't install WhatsApp, the sender won't be able to send the message.
This fact can be annoying and isn’t necessarily a good thing.
Very few - if any - of the OTT platforms out there are compatible with others; instead, they are in competition. What this means is that one group of friends is likely to use one platform, while another group will be relying on something else entirely.
This is far from ideal.
Why Should You Care About Messaging Security
With the fact that anyone can send SMS messages, the service has long been tied with scams and ghost texting. Because of these, people should question how secure text messages are in general.
What you should know is that, text messages, no matter what medium they use, involve a multi-step process.
In SMS services, a message might be encrypted from your phone to the first cell tower, but it may not be encrypted after that. Your SMSC may keep the message even if both the sender and recipient deleted it. Due to the lack of encryption, people with interest can search for weak points along the virtual path between the sender and the recipient.
For those who send private messages or sensitive data, SMS couldn't be the method to rely on.
Securing text messages isn't always protecting secrets, as it's more about ensuring personal privacy for everyone involved.
And when considering OTT apps, despite being more modern and more secured, they are also not foolproof.
Hackers have managed to develop ways to intercept web traffic, create sophisticated phishing scams, and develop complex malware to steal information. By collecting all the available information from a target, hackers can gather and arrange them as puzzles, as a workaround to get even more sensitive information.
Not to mention that OTT apps also have bugs that are yet to be discovered.
Given the propensity for and variety of attacks, it makes sense for you to always use two-factor authentication on apps, and use messaging apps that offer end-to-end encryption.
Again, no technology is a 100% safe, as products should have flaws that are yet to be discovered, or hackers yet having developed method to exploit certain security holes. But when considering the fact that hacks are more than plenty, it's wise for anyone to embrace newer technologies that promise better security.
With more modern technologies and less parties involved, the process of sending information should be more secured than it used to.
