Smartphone infection can come in many forms. But in some cases, the method of infections using old technology can often be worse.
At least for users of mobile phones, as hackers have started leveraging SIM highjacking to intercept messages to breach two-factor authentication, for example. Unfortunately for users, SIM jacker isn't the only SIM-based attack that could put phone users at risk.
According to Ginno Security Lab on its report, another exploit called 'WIBattack', can compromise the WIB (Wireless Internet Browser) app on some SIM cards to take control of key phone functions.
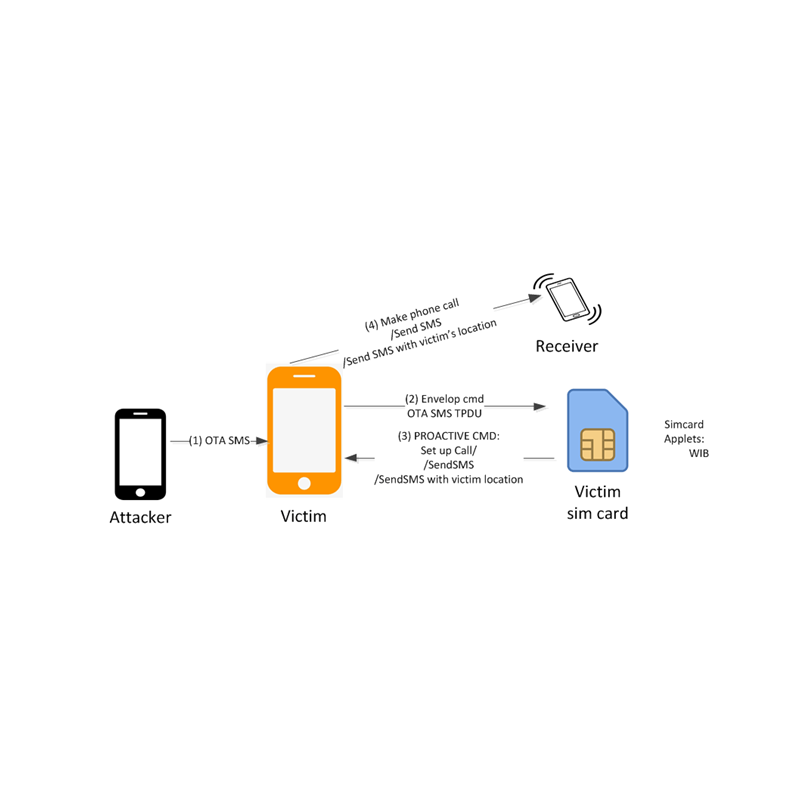
Like its counterpart, which was discovered by AdaptiveMobile Security earlier this September 2019, the attack infects phones through a carefully formatted SMS text that runs malicious instructions on victims' SIM cards.
If successful, the attackers can send texts, start calls, point web browser to specific websites, display text, receive IMEI and receive the victims' location information.
This vulnerability is present because some cellular operators use dynamic SIM toolkit as an alternative to static SIM toolkit application.
Using this, operators can show menus and user dialogues, that are generated on-the-fly, and based on the information provided by the providers' central server. SIM applications with this functionality are generally referred to as SIM-browsers or µ-browsers.
According to the researchers, there are two browsers available, and the one they are concerned, is the Wireless Internet Browser (WIB), which was the first successful browser released and promoted on the market by SmartTrust.
WIB is the market leader for SIM toolkit based browsing. And with WIB-enabled SIM, phones can show menus that are coded on the SIM. This menu allows interactions, and can be managed and updated using Over The Air (OTA) services.
And this is where the vulnerability resides: attackers can use this OTA to send command to the victims' phones.
According to the researchers, "more than 85 mobile operators worldwide are using SmartTrust technology to diversify their service offerings and open new revenue streams by launching enhanced SMS services, controlling mobile end-user applications and managing the entire life cycle of the SIM/USIM.”
And this goes worse, as "operators of more than 200 networks worldwide [...] rely upon SmartTrust technology to address the unique business challenges of today’s mobile markets. With a complete portfolio of products and services, which facilitate the management of the entire lifecycle for SIMs, handsets and services as well as Dynamic Roaming Steering, SmartTrust delivers the tools for successfully managing the subscriber experience."
What this means, WIBattack can let attackers globally take control of hundreds of millions of the victim mobile phones worldwide.
The researchers have reported the vulnerability in WIB to The GSM Association. But according to them, it's not clear that the industry body is doing anything to address this issue. This is why they have suggested several things to do to prevent users in becoming sitting targets. This includes:
Network-sides
- SMS Home Routing.
- Filter OTA SMS.
- OTA update to SIM card to update MSL or to remove WIB.
- Should have security guideline and SIM-scanning tool to check security of SIM card samples.
- if the SIM card has the vulnerabilities, providers should change this for a newer and secured SIM card.
End-user sides:
- Scan their SIM card for this vulnerabiilty using SIMtester.
- If SIM card has vulnerabilities, users should buy a secured SIM card because network providers could not protect unsecured SIM card when users go roaming on other networks.