There were days when everything was offline. Our computers should first be connected to the internet manually, and there weren't any smartphones around.
As technology evolved, it changes how we use devices.
Our computers, as long as they are on, they are also online, and so does our smartphone. In the era where everything is practically connected to the internet, the change should also evolved the way we interpret security and privacy.
With the many things we do and store on our devices, and with the interactions we make on the internet, data transaction happens all the time. This information passes through those invisible networks from all around the world, from and to our devices.
And this is where things get interesting for hackers.
As services and data are abundance, there are more holes and vulnerabilities that are either unseen or left open. Hackers can hack themselves by getting through those weaknesses to do whatever they want.
But what we tend to forget is that, our biggest enemy in security is not the weaknesses in our devices. In fact, it's ourselves. This is where hackers use what is called 'social engineering'.
Social Engineering That Exploits Human Vulnerabilities
Social engineering is a skill that exploits some common human vulnerabilities. Hackers can make use of this skill to gain access to sensitive and secure credentials by manipulating through human involvement and interaction, even if the system itself is a 100 percent secured.
To do this, hackers manipulate human psychology to lure unknowing victims into committing mistakes, which will then allow the hackers to break into their secure routine, in which will result in the exposure of the victims' sensitive data.
Social engineering can be difficult to initiate, and can also take a lot longer than needed, as hackers need to go through a series of steps before harming the victims. The steps may vary from one suspect to another, as more cautious people would require the hackers to do more steps. But overall, the process of gathering information of the soon-to-be victims remains the same.
After the relevant information about the soon-to-be victims is gathered, the hackers proceed to the second step, which is gaining victims' trust which eventually allows the victims to be manipulated. And lastly, when the victims have been manipulated, they will reveal their sensitive information willingly but without knowing that they are actually being scammed.
The whole process of social engineering revolves around the aspect of mistakes committed by humans. Here, hackers exploit weaknesses in victims' personality which makes them have a false sense of security with the attackers giving them the green light to get the information they want.
The main techniques of social engineering involves four major types:
Phishing
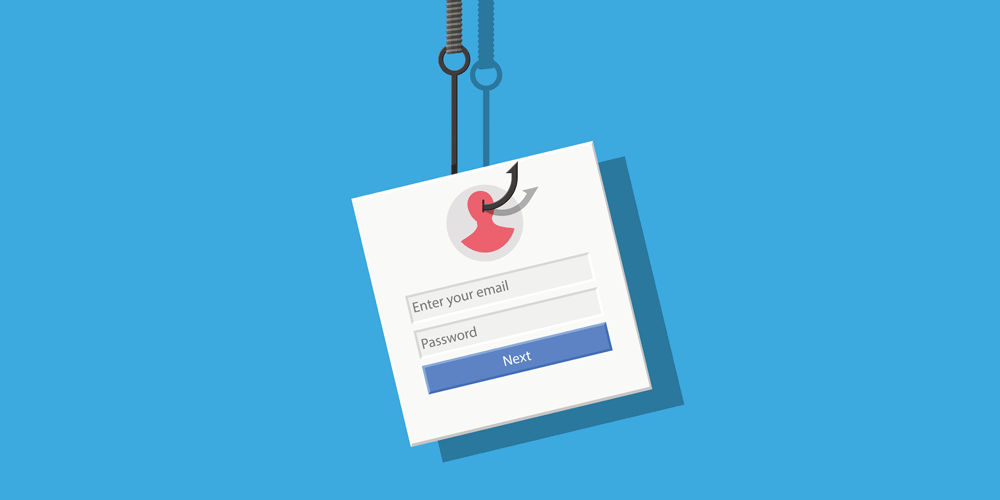
Phishing is one of the most famous social security engineering attack types, and also the most common.
To make this attack happen, hackers target victims through different mediums, such as emails, fake websites with similar URLs as legitimate websites, which are all meant to complete the attack. Phishing scams are mostly initiated by hackers impersonating a well-known or familiar organization used by the victim.
The strategy here is to encourage unsuspecting victims to open malicious links to download malicious software or to reveal sensitive information.
For example, users may receive an email on behalf of a company/organization/online services they have interacted with. To initiate the hack, the hackers may notify that the service the users use have its privacy policy changed, and requires the users to change their password by visiting the link embedded in the email.
With the email being perfectly crafted, users that are familiar with the services they use, tend to be vulnerable: they rarely check what the email address looks like and just proceed to open the email and the link without any precautions.
Clicking on the link will open a fake website, usually with fields to input users' login credentials. The page can be perfectly made to mimic the login page of the legitimate service, down to the very pixels. Entering the sensitive information and enter, will send that information straight to the hackers.
Related to phishing is smishing, which is the act of using SMS text messaging to lure victims into a specific course of action, and vishing, which is also known as "voice phishing".
Baiting

Just how the name suggest, baiting uses attributes of an individual’s personality against them. Hackers lure victims into a trap, in which the hackers can exploit everything the victims have. Usually, this method is done by using malware.
The most difficult part is to get that malware installed on the victims' device. If hackers have the devices on their hands, things would be easier, but in this case, social engineering involves the hackers in trying to make everything seems blissful but ending up with users losing their credentials.
Or worse, like infecting the victims' device with deadly malware which can do a lot more damage.
There are two ways hackers can do this.
- Physical: hackers can use physical hardware like a flash drive, and hope for a victim to plug it into their computer. If that happens, it will install a malware, which would allow the hackers to easily break into the system.
- Online: This requires victims to download some malicious software on the web. There are numerous methods that can be utilized, as it can happen through an email, fake website or a series of ads and redirection.
This baiting method is also related to quid pro quo (something for something).
In this strategy, hackers call a random number at a company and claim to be from a technical support. If the victim falls into the trap, the victim would be grateful that someone is calling back to help them. The hackers "help" the victim to solve the problem and, in the process, have the victim types some command that give the hackers the access, or the ability to launch malware.
Scareware
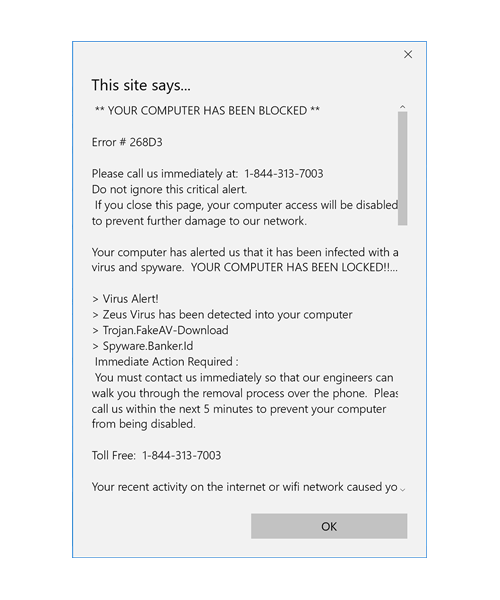
Another common type, is using scareware.
Scareware is a type of application that makes victims see fake threats on their system. This false notification is meant to lure victims into seeing an illusion that their system is under attack or affected by malware, when in fact it doesn't.
The scareware asks the victims to download a specific software which is “supposed” to remove the malware.
However, the software in question doesn't contain any fixes, as it's sole intention is to disrupt things.
The most common example of scareware would be those popup websites that display threats on browser screen like "Your computer is infected, please download the software below to remove it." Commencing will lead the unsuspecting victims into downloading a malware.
Scareware can also spread through spam emails.
Pretexting

Pretexting is another type of attack used by hackers, but is relatively less common as it is more difficult to initiate.
The attack involves the hackers in creating a really good yet believable strategy to lure victims into a trap to extract information from them. The scam is initiated with the perpetrator impersonating a high profile officer of an organization pretending to need the victims' information to perform a critical task.
The hackers can also impersonate family members, colleagues, or acquaintances that "ask" the victims for sensitive information to get what they want.
For example, hackers can impersonate high ranking officials, like police officers, tax officials, or other people with authority, and ask incredibly confidential questions. In order to sound more believable, the attackers often impersonate by saying some things only known personally.
Like if the soon-to-be victims have been on vacation. The hackers may have got the idea after scouting some information about the soon-to-be victims to sound believable. All sort of important and sensitive information is previously gathered to commence this attack, which can include personal addresses, phone numbers even bank account credentials.
While this method is less common, it can be more devastating.
For example, if you fall as a victim and the hackers have extracted your email login credentials, the hackers can send the same attack to people on your contact list. In this case, the hackers impersonating you can send the next wave of pretexting attacks to your contact list. Your contact list that sees your email address, will believe that you were the one who sent the email, and will likely fall into the same trap.
The Ways To Prevent Social Engineering Hacks
There are many different ways that you can use to prevent yourselves from falling as victims to these social engineering hacks, and having a strong mind presence should help you the most in identifying such threats.
Know that:
- Anyone can send you an email, so treat all emails as suspicious, especially those that ask for sensitive information or have links on them. Here, you need to investigate everything from the sender's email, to the link that is embedded. Never rush to reply, forward or click on anything.
- Spam filters should help you a lot in filtering out dangerous emails. If any of those emails do pass the filtering process land on your inbox, your are urged to remove those suspicious messages immediately.
- Securing all your operational devices is always a plus. You can use antivirus and firewall program for every platform that a device uses whether it be, Android, Windows, Mac or Linux. Installing one can keep you safe from unwanted malware, if it ever get into your system.
- Keeping your operating system updated is recommended. Almost every OS releases updates once in a while to patch security vulnerabilities, and keeping your system up-to-date will ensure that you have installed all the necessary protections against hacks.
- It's extremely rare for services that offer popular products to contact you individually. So popups pretending to be tech giants contacting you would be most likely a scam. Tech giants won't be contacting you individually to try and fix your problem because it's expensive to do so, and will also waste their time. Instead, they will release security updates to patch the vulnerabilities, to then notify users of the news.