Web browser is the gateway to the World Wide Web. And that is why securing your online activities should start from securing your web browser.
When downloaded and installed, web browsers come equipped and already set with their default settings, which may not offer the very best protection. Most people unfortunately, don't really bother to dig deep into the settings to customize things, or to improve their web browser's capabilities.
These people are missing a lot of chances.
For example, browsers can allow location tracking and cookies to popup. If these are turned on, your browsing security can be compromised in unintended ways.
Because most certainly that every devices that connect to the web have web browsers installed, here are some common and easy ways to improve your web browsers' security.

Configure Your Web Browser's Privacy Settings
Configuring your web browser's privacy settings is one of the most important things you can do to secure your web browser. By default, many browser settings leave your personal data exposed. At a minimum, you should at least:
Disable pop-ups and redirections: Pop-ups and redirects are annoying, and can also be used to spread malware. Try disabling these.
Don't allow automatic downloads: Files downloaded from the internet can contain malware, so it is wise to set your browser to always prompt you before downloading anything.
Keep cookies in check: Delete cookies after browsing and turn off third-party access to cookies.
Restrict access to your location, camera, and microphone: Make sure your browser asks for permission before accessing these features.
Deactivate ActiveX: ActiveX is considered outdated, and poses security risks. Also consider deactivating Flash, and JavaScript, if needed.
Turn on 'Send a Do Not Track request': This should help prevent websites from tracking you, but it's not a guarantee.
Keep Your Web Browser Updated To The Newest Version
A no brainer. Even if you use the best and the most secure web browsers available, it won't be able to protect you from the latest threats if it's outdated.
Web browsers are updated frequently, not only to introduce more features and capabilities, but to also patch bugs and improve security.
Every browser is a little different when it comes to software updates, with some automatically push updates, and the others require your consent. This is why you need to frequently check for your browser's newer version manually.
Use Private Or Incognito Mode
Most modern web browsers have what it's called 'private' or 'incognito' browsing mode.
This mode prevents the browser to record your web browsing history, browser cache, form data and cookies. These information are generated while you browse, kept on individual tabs, and will be discarded when the tab or browser is closed.
In other words, your browsing activities will be deleted as soon as you stop browsing.
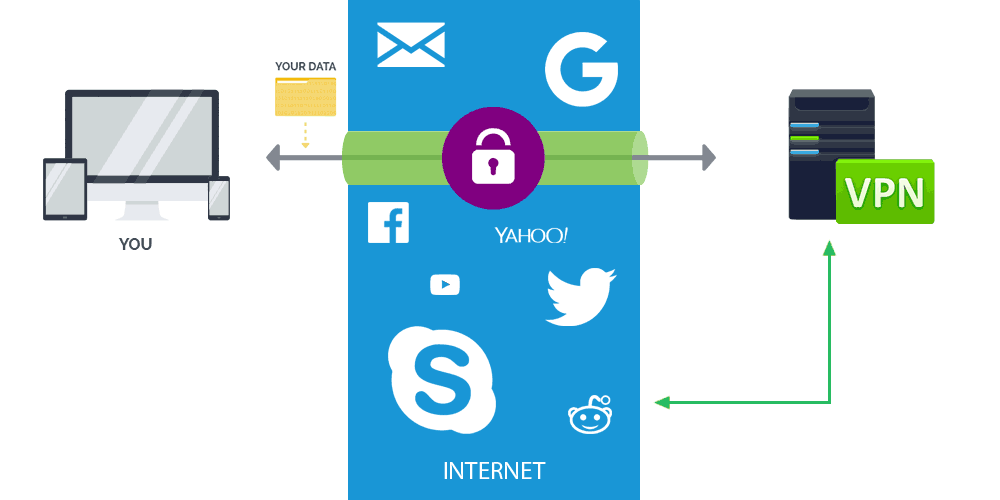
However, your IP address and activities can still be tracked by the websites you're visiting, and by the internet service provider you're using. If you want to completely hide your IP address, location, identity, and activities when browsing the web, consider using a VPN service.

Use Browser Security Extensions
Many modern web browsers allow your to install additional security measures that come in the form of extensions.
These add-ons can help you bolster your browser's security and privacy. These extensions can come from third parties, so you need to make sure that the extensions are from reputable developers, and/or endorsed by the browser you're using.
Make sure that you enable the extensions' automatic updates to keep them updated at all times.
Use VPN
Even the most secure browser updated to the latest version cannot keep your browsing activities truly secure or private from your ISP, employer, or school.
This is why you should consider using a VPN service, which tunnels your connection, encrypts your data, and secure your activities. VPNs in general:
- Disguises your IP address and location: VPNs spoof your IP address and location, so you can't be tracked by your ISP (internet service provider), or the sites you're visiting.
- Encapsulates your web traffic: With a VPN, all your data packets are hidden inside additional packets, so your data moves in a private "tunnel" over unsecured networks.
- Encrypts your web traffic: VPN services encrypts your data to make it virtually impossible for anyone to know what you're doing. This is especially important when browsing over public Wi-Fi.
What you should know when using VPN is that, you're allowing that VPN provider to manage, control and direct your traffic.
In other words, your original ISP is replaced by the VPN you're using. This is why you need to make sure you use trusted VPN providers that don't log your activities.
Further reading: Staying Anonymous: Proxy, VPN Or Tor?
Choose A Secure Web Browser
From Google Chrome, Apple Safari, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Internet Explorer/Edge, Opera and others are popular and have their own fans and user base.
As modern browsers from famous developers, they are updated frequently, have many features and capabilities, and are probably the first to introduce new technologies. But that doesn't mean your choices end there.
There are other browsers in the market, with some dedicated to privacy. For example, the Iridium browser, GNU IceCat browser, Tor browser, and more.
Use Common Sense When Browsing
Last but not least, even if you follow all of the above, you can still fall as a victim to bad actors, hackers and malicious software.
This is because no matter which browser you use, there's no such thing as a 100% secure web browser on its own. This is why you need to always be cautious, and use your common sense when browsing the internet.
This includes, and not limited to:
- Never download files from sites or sources that provide 'hacked', 'free', and 'nulled' software. These sites can host tons of malware.
- Never open attachments or links sent from unknown sender. Many hacks start from here.
- Check for HTTPS to make sure that your browser's connection to the site your visiting is secured.
- Be wary of shortened links because they can hide bad links.
- Log out of any session after using it. You may not know who will be the next person using the device you're currently using.
Related: In The Age Of Mobile Computing, Cybersecurity Is All About Hardware, Software And You